








Compliance - Records of processing
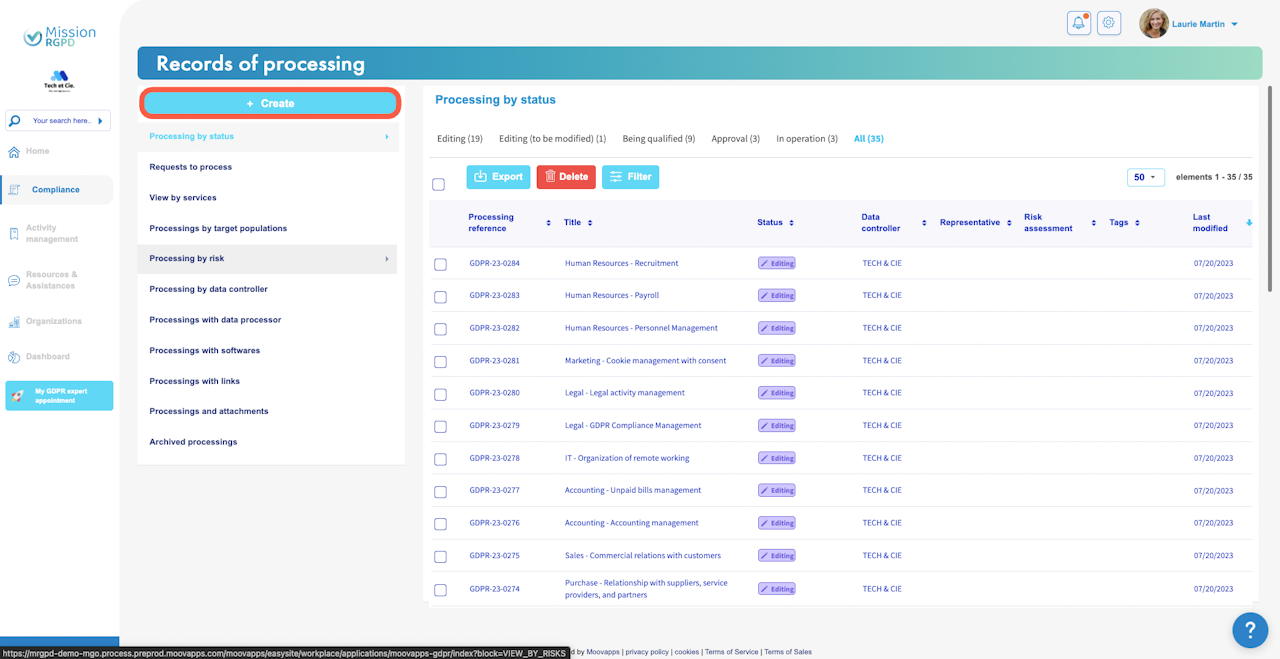
To create a new processing activity directly in Mission RGPD, click on the Create button from the list of processes (Compliance Menu > Records of processing).
Mission RGPD guides you through the declaration of your processing activities using a form to be filled out.

Overview of a processing record
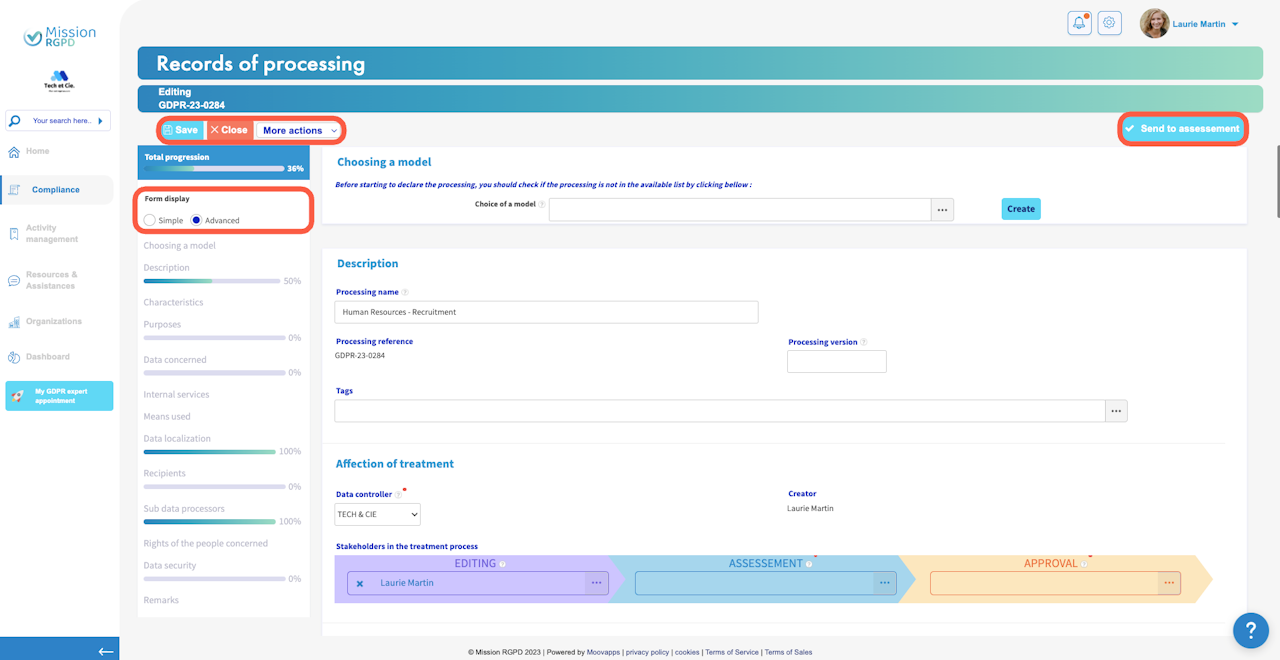
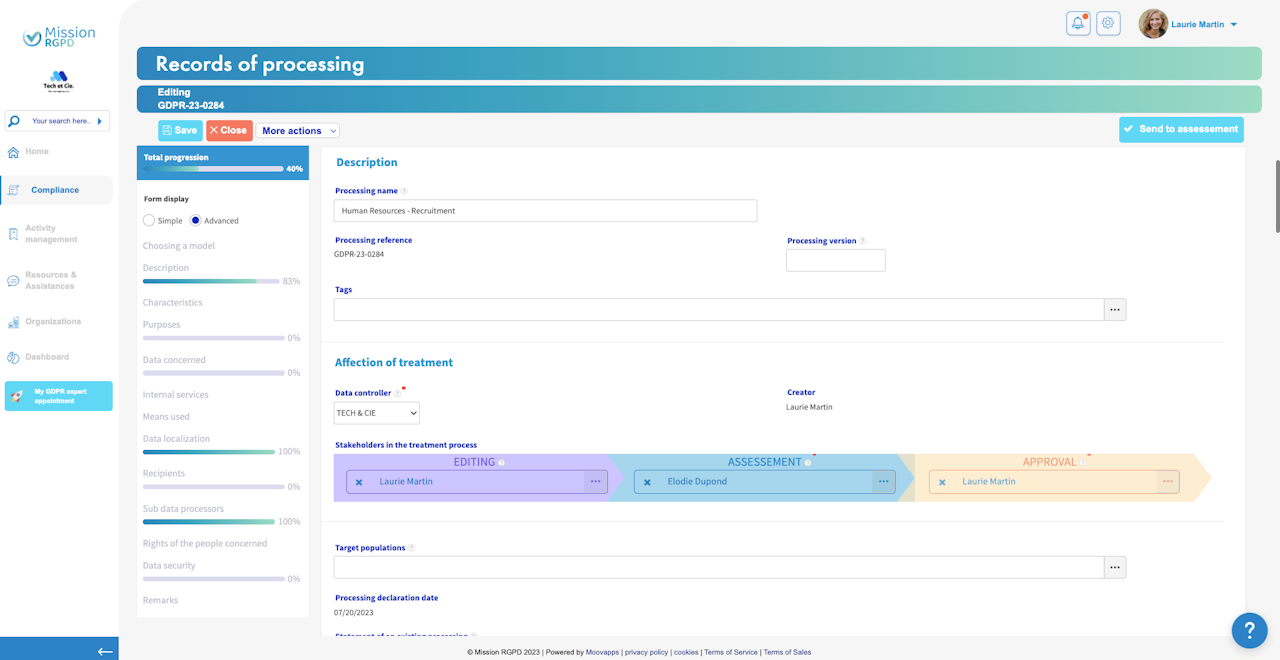
At the top of your form, you will find the following buttons:
Top-left corner:
The "Save" button allows you to save your modifications at any time.
The "Close" button allows you to close your processing record (you can return to it at any time, provided you have saved your changes).
The "More actions" button allows you to access various actions related to your processing record.
Top-right corner:
The "Send for qualification" button allows you to proceed to the next step of the processing record.
On the left side of your form, you will find a navigation menu.
This menu enables you to:
Track your progress as you complete the form.
Select the type of form you wish to create:

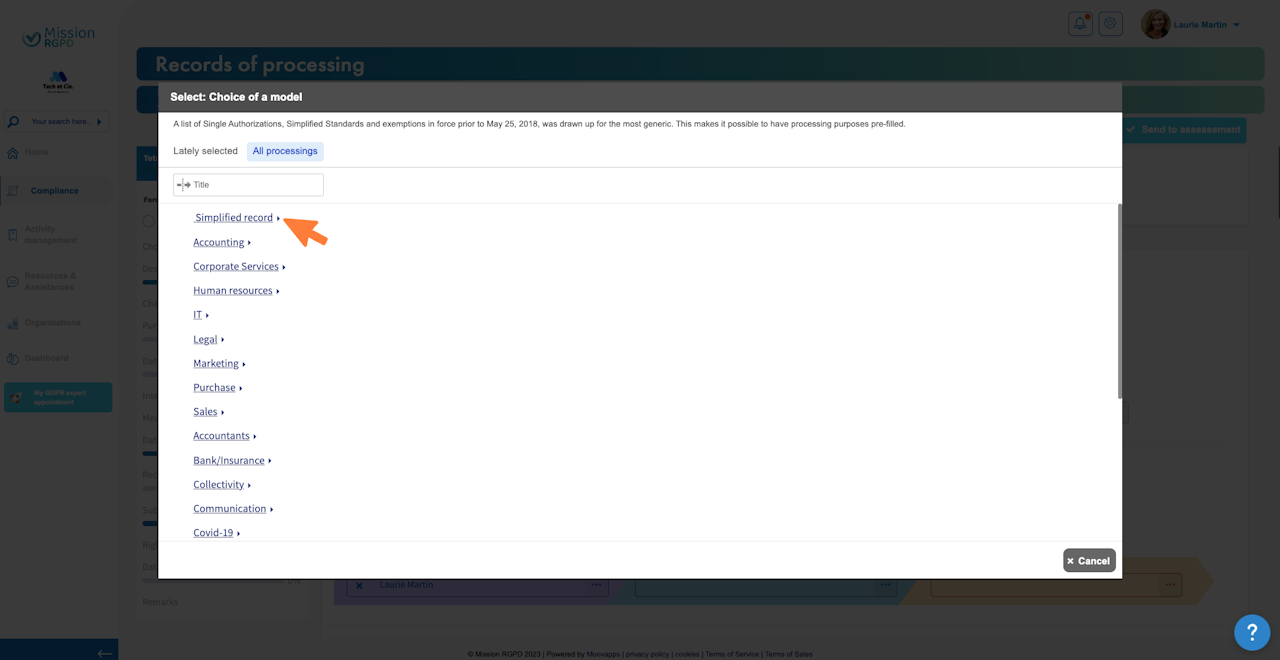
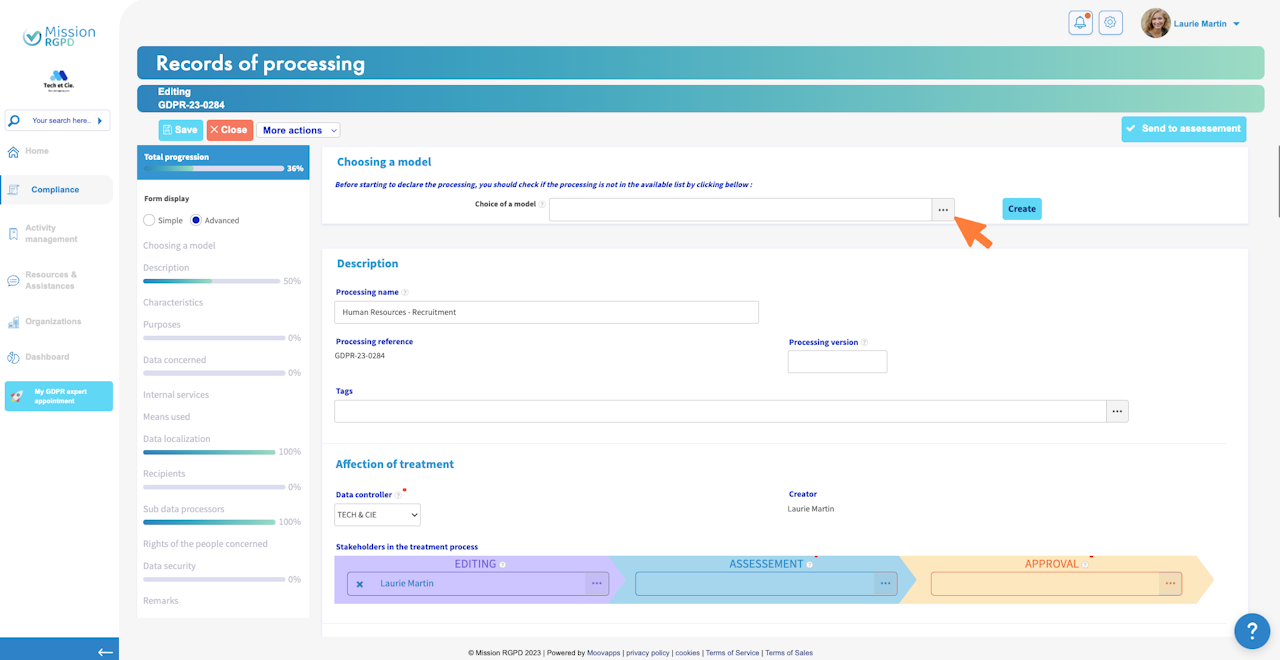
Selecting a processing record template from our repository
Mission RGPD has developed a set of processing record templates. You can choose a template that matches your needs, and Mission RGPD will pre-fill your form. All you have to do is complete and/or customize it according to your requirements.
This allows you to have information about the characteristics of personal data processing activities.

Processing description
Title: Name of your treatment
Reference: This field is generated by Mission RGPD. It is the unique identifier of your treatment. You can use it to find your treatment from the search bar or filter your treatment lists.
Treatment version (optional): Allows you to indicate if the treatment has been modified.
Data Controller: The organization responsible for the treatment, which is the legal entity (corporate entity) to which the treatment is attached.

Affectation of processing
Stakeholders in the treatment process:
Editing: This is the stage during which the user writes the record by completing the various fields. This person also receives modification requests if the treatment needs to be updated.
Assessement: This stage is dedicated to assessing the risk. The user who take action at this stage is usually the DPO/GDPR referent. The person reads what was written in the first stage (editing) and evaluates the risk associated with the treatment.
Approval: This stage involves reviewing the previous stages (editing and assessement). The user becomes aware of the risk and then validates or rejects the processing. Once it's validated, the processing becomes active, meaning it is current and ongoing as described in the editing stage.
Target Population(s): Typology of person whose data is used for the processing (e.g., employees, customers, prospects, etc.).
Statement of an existing processing: Is it a new data processing, or does it already exist?
Desired processing implementation date: When do you wish to start the processing? The date provided can be approximate.
Joint controllers: Organization that jointly determines the objectives of the treatment along with the Data Controller.

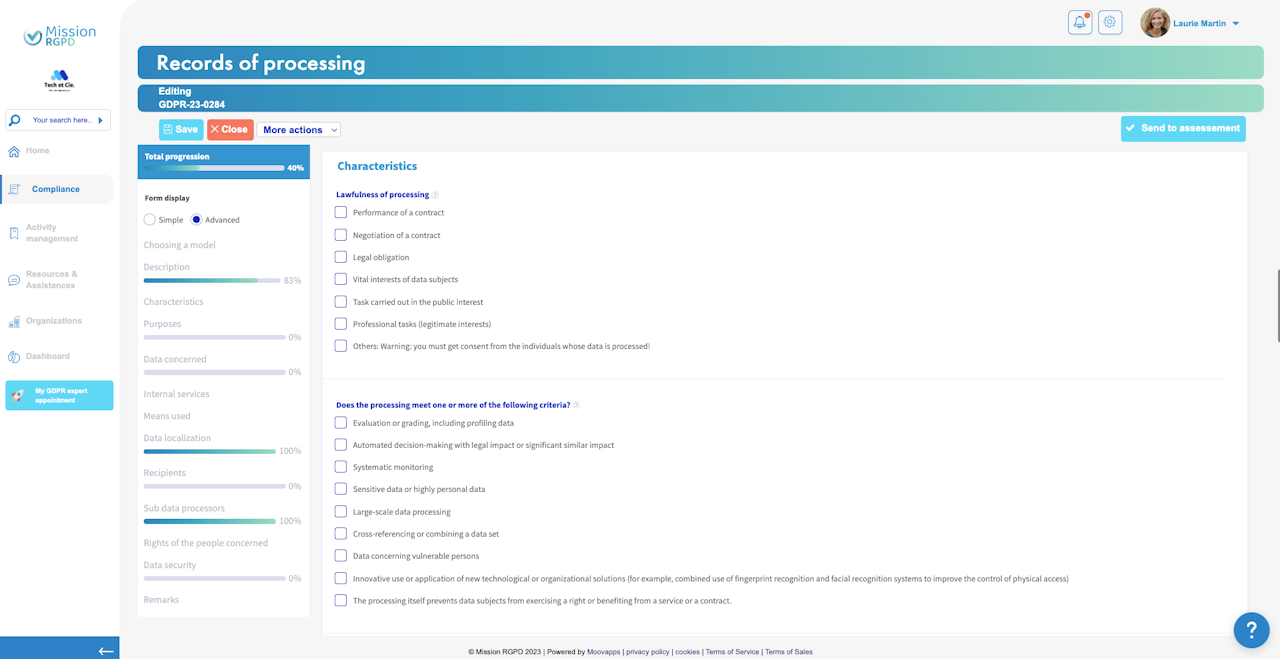
Characteristics of processing (1)
Lawfulness of processing
For a processing to be legal, it must be based on a legal basis:
Execution of a contract: Necessary in the context of a contract. For example, using the postal address to deliver a product.
Negotiation of a contract: Refers to cases where a contract is being considered.
Legal obligation: The obligation must stem from European legislation or legislation of a Member State.
Vital interests of data subjects: The processing is lawful when the vital interests of a person are at stake. For example, medical appointments.
Performance of a task carried out in the public interest: The treatment falls under the exercise of public authority.
Legitimate interests: The processing is necessary for the legitimate interests of the Data Controller unless the interests or rights of the data subject prevail. For example, establishing a list of defaulting customers.
Consent: The data subject's consent must be given for one or more specific purposes. It must be a clear, affirmative action, meaning the person actively accepts the treatment.

Characteristics of processing (2)
Does the processing meet one or more of the following criteria?
These criteria determine whether a privacy impact assessment (PIA) will be required before implementing the treatment.
Evaluation or profiling activities: The processing involves assessing a person's performance, preferences, or interests, for example.
Automated decision-making with legal or similar significant effects: This processing could lead to exclusion or discrimination for the individuals concerned.
Systematic monitoring: The treatment is used to observe or monitor individuals. The collection may take place without the individuals' knowledge of who is collecting their data and for what purposes. For example, public surveillance cameras.
Sensitive or highly personal data: These data are covered by Article 9 of the Regulation, concerning health, religion, political opinions, data on offenses, or criminal convictions. It might be used for processing linked to human ressources (health data).
Large-scale data processing: This criteria considers the number of data subjects, either in absolute terms or relative to the population considered. The geographical scope may also be taken into account.
Cross-referencing or combining a data set: Data that would come from two separate treatments and exceed the data subjects' expectations.
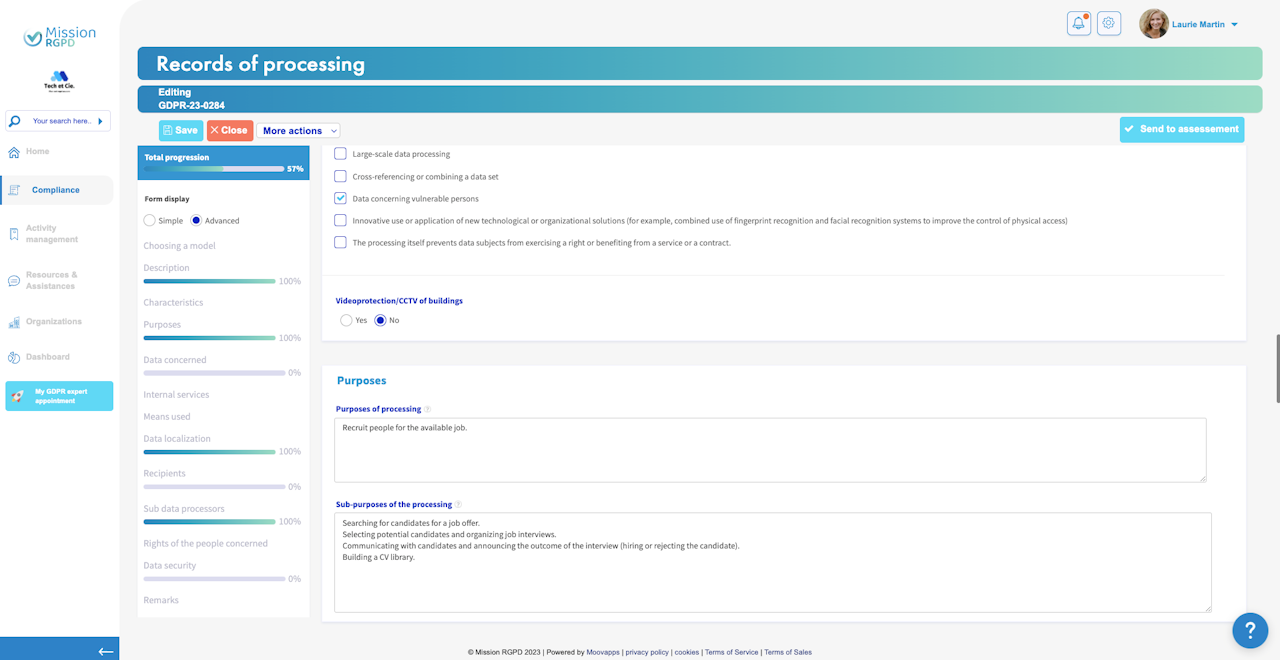
Data concerning vulnerable persons: This includes individuals for whom an imbalance in the relationship with the Data Controller can be identified. For example, employees, minors, incapable adults, patients, etc.
Innovative use or application of new technological or organizational solutions: If the technology could involve new forms of data collection or use compared to current practice. For example, new connected devices with innovative use, IA, etc.
The processing itself prevents data subjects from exercising a right or benefiting from a service or contract: The processing concerns operations that allow, authorize, modify, or refuse access to a service or the conclusion of a contract.

Characteristics of processing (3)
Videoprotection/CCTV of a building:
This section allows to detail the use of cameras to protect a building, including the number of cameras used, whether sound is recorded, whether cameras have covers, and the date of any prefectural authorization, if applicable.

Processing purposes
Processing purposes:
These are the objectives pursued by the processing. It answer the questions: Why do I use the data?
Sub-purposes of the processing:
These are additional use of the data.

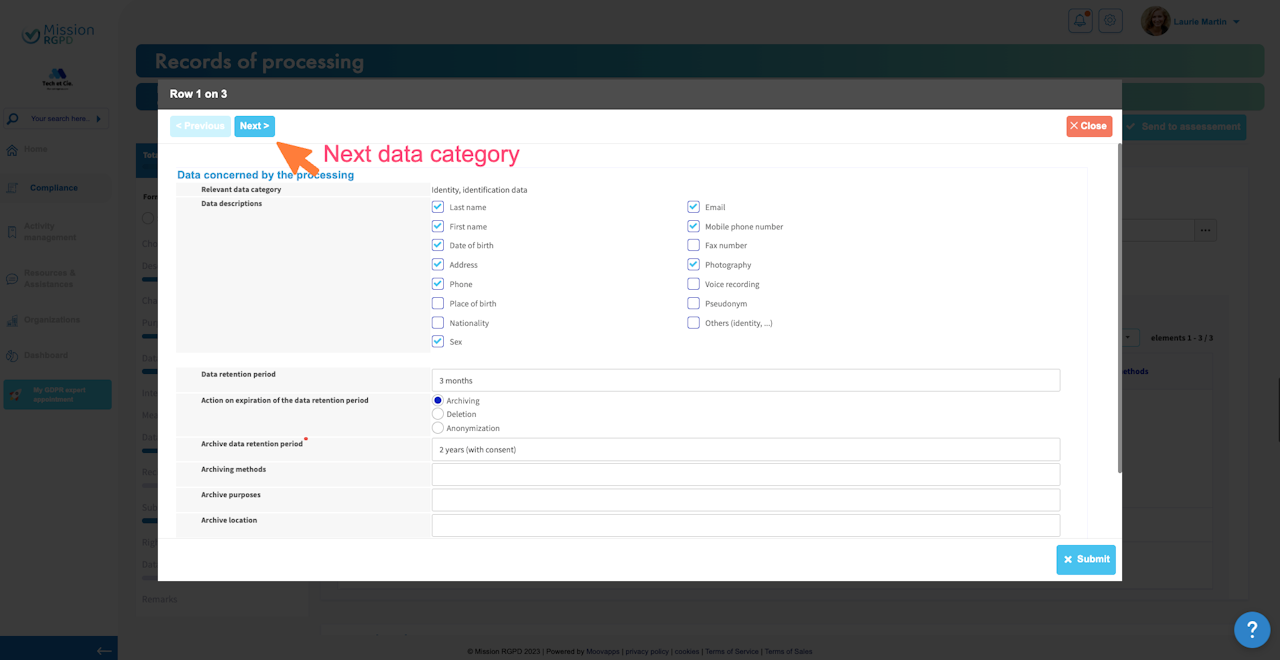
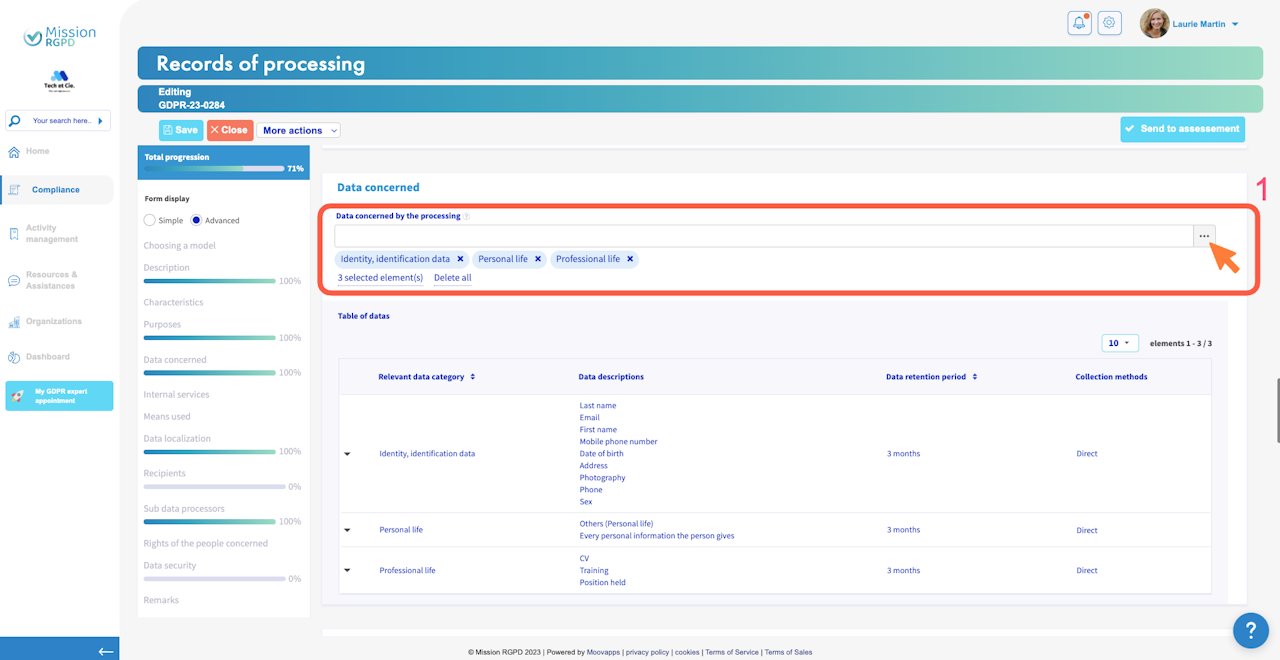
Data concerned by the processing
Data concerned by the processing:
These are the data used for the processing.
First, you need to select data categories.
Then, click to "Access" to edit the table of datas.
Finally, specify for each data category :
Data descriptions,
Retention period, and detail if at the end of processing you archive, delete ou anonymize the data. If you choose "Archiving" you must precise the archives' retention period,
Data collection method, it refers to how you obtained the data, whether directly (e.g., provided by the individual via a form) or indirectly (e.g., from another service).

Internal services
Select the department who does the processing.

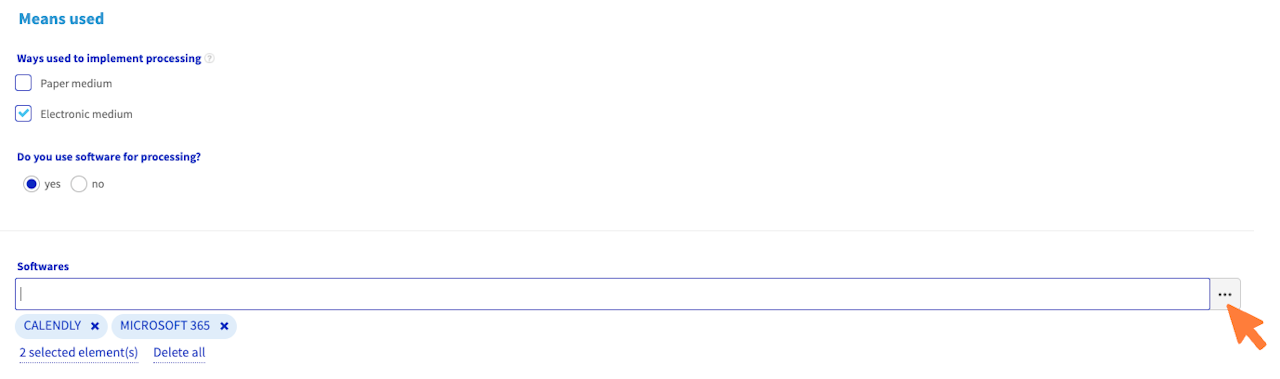
Means used for the processing
Select "Paper" if you process the data on a printed document (for example if you collect the data with a printed form).
Choose "Electronic" if you use an electronic device, such as a software, to process the data.
If you select "Electronic" then you declare you use a software, you will be able to name it.

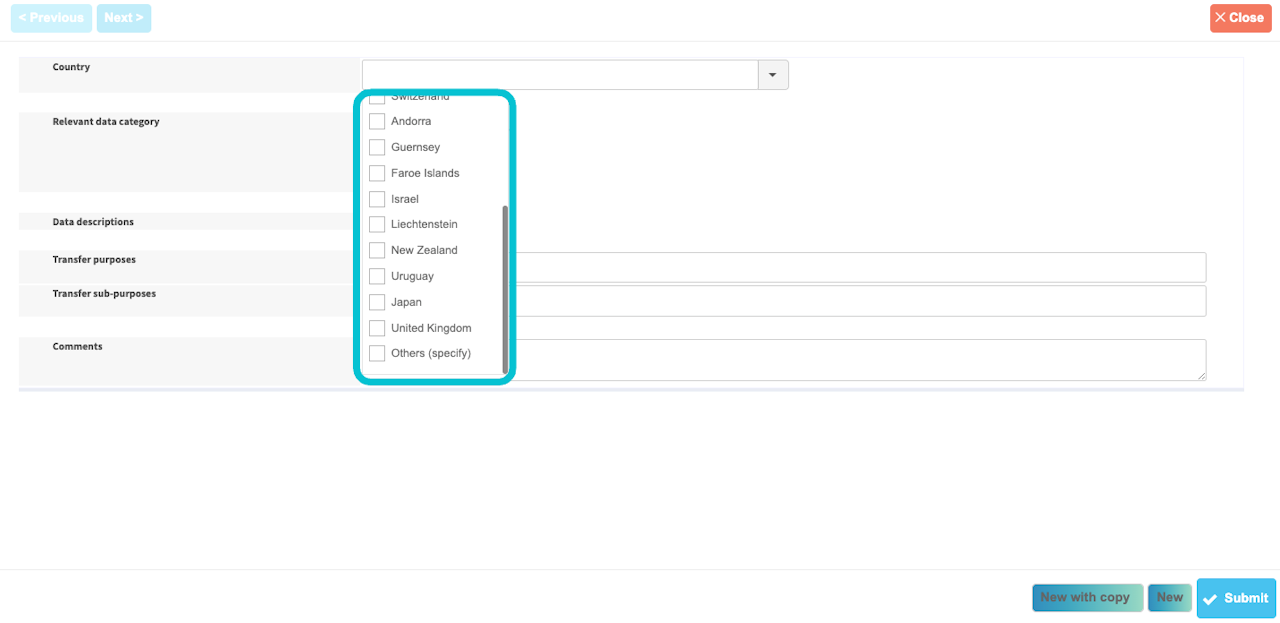
Data localization
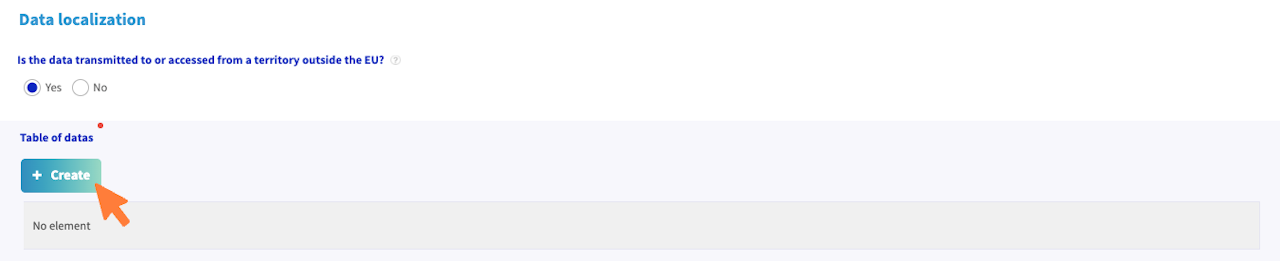
Data localization
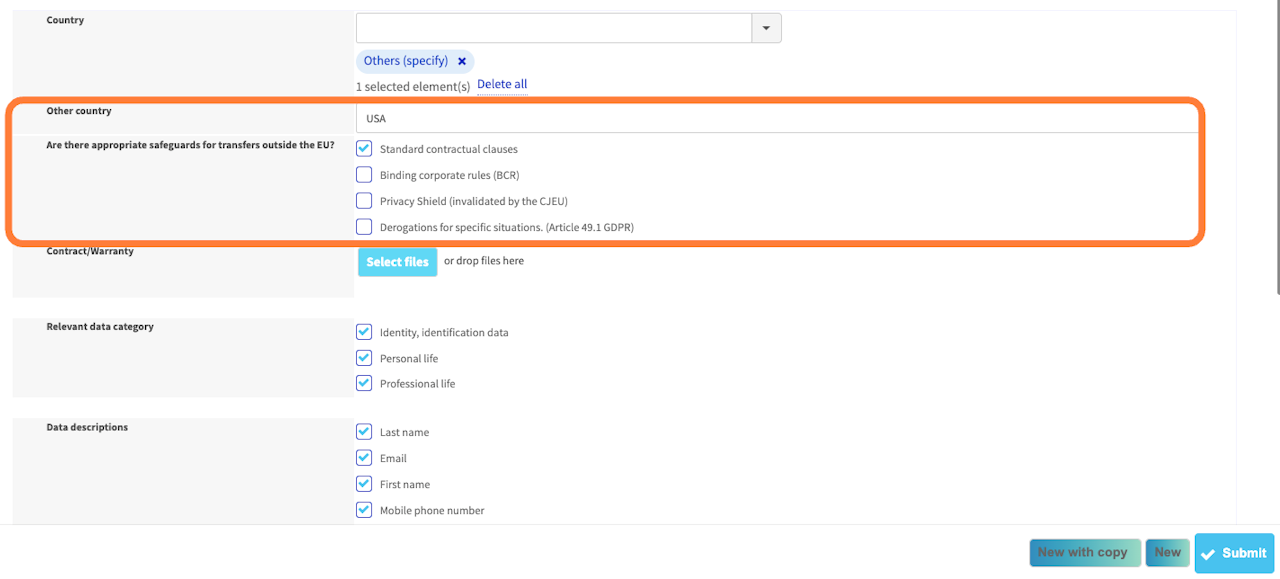
Is data transferred or accessible from a state located outside the European Union?
If so, choose "Yes" and click to "Create" to open the table of data. Then you need to select a country.
The country where you transfer data is on the list: transfer is based on an adequacy decision so you don't need any appropriate safeguards.
The country where you transfer data isn't on the list, select "Other (specify)": you need to find which appropriate safeguards applies.
(Optional) Precise the category or categories of data that are transferred.
Finally, you need to document the purpose and any sub-purposes of the data transfer. For example the transfer might occur because of the use of a software.

Recipients of the processing
Internal recipients:
These are the departments or services within the organization that are recipients of the data, meaning they have access to the data and process it.
External recipients :
These are services, organizations, or entities that are recipients of this data.
(Optinal) In both cases, you can document which data category the recipients, whether internal or external, have access to. You can also specify why these recipients have access to the data.

Sub data processors
Use of one/more processor(s):
According to the GDPR, a processor (subcontractor) is the entity/organization that processes data on behalf and under the authority of a data controller.
If you call upon a subcontractor, choose "Yes". Then, select one or several processors on the list.
(Optional) Finally, you can open the table of data to specify which data category each processor have access to and the reasons for such access.

Rights of the people concerned
How do people whose data is being processed are informed about their rights? You can select "Other" if the answer isn't on the list.
Function of the person or department to whom the data subject rights requests are sent (specify):
It is necessary to specify the role or the department responsible to handle requests related to individuals' rights.
Data subject rights procedure (specify):
Specify how data subjects can exercise their rights. For example, through email, a form on the website (available on Mission RGPD), or by postal mail.

Data security
Document the measures taken to guarantee data security.

Remarks
This section allows you to leave a comments or additional attachments.